 I was waiting around a bit for my younger son’s doctor’s appointment this morning, so I decided to edit a book. I finished it just now, it’s called Another Introduction to Ray Tracing. It’s 471 pages in book form. You can download it for free, or order a paperback copy from PediaPress for $22.84 plus shipping. I won’t earn a dime from it, but since it took me less than two hours to make, no problem.
I was waiting around a bit for my younger son’s doctor’s appointment this morning, so I decided to edit a book. I finished it just now, it’s called Another Introduction to Ray Tracing. It’s 471 pages in book form. You can download it for free, or order a paperback copy from PediaPress for $22.84 plus shipping. I won’t earn a dime from it, but since it took me less than two hours to make, no problem.
So what’s happening here? Due to investigating Alphascript and Betascript publishing a month ago, reporting it on Slashdot, and following up on a lot of great comments, I learnt a number of interesting tidbits. Here’s a rundown.
First, VDM Publishing itself is sort of a vanity press, but with no cost to the author. It seeks out authors of PhD theses and similar, asking for permission to publish. This is not all that unreasonable: because the works are only published on demand, the authors do not have to pay anything, they even get a few hardcopies for free. Here’s an example from our field that I reported on in February. That said, it’s mostly a win for VDM Publishing, who charge steep prices for the resulting works. Such not-quite-books mix in with other books on Amazon. It takes a bit of searching to realize that the work is a thesis and likely could be downloaded for free. A bit misleading, perhaps, but not all that horrifying. Caveat Emptor.
VDM Publishing also has an imprint called LAP, Lambert Academic Press, which does the same thing, publishing theses such as this one by Nasim Sedaghat. With a little Googling you can find Nasim, and then find the related paper for free.
VDM’s imprints Alphascript and Betascript Publishing I’ve already described, they’re little more than random repackagers of Wikipedia articles. Here’s an example book. I posted one-star reviews for a few of these books on Amazon; what’s funny is that the owner of the firm actually responded to my criticism (with a one-size-fits-all response in slightly broken English).
Four weeks ago Alphascript had 38,909 and Betascript 18,289 books listed on Amazon. To my surprise they now have 39,817 and 18,295 books, a total increase of only (only!) 914 new books – looks like they’re slowing down. They’ll have to work hard to catch up with Philip M. Parker’s 107,182 books or his publishing firm ICON Group International, with 473,668 books. The New York Times has an interesting article about this guy.
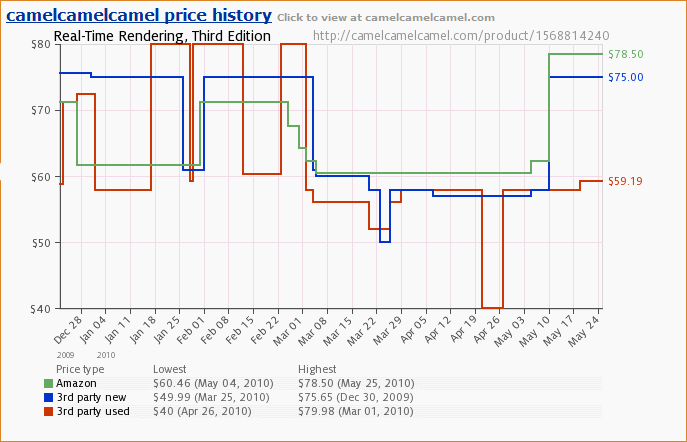
Betascript Publishing has two books found on Amazon related to ray tracing: Ray Tracing (Graphics) and Rasterization (which includes a section on ray tracing). The ray tracing book is 88 pages long and $46, more than 50 cents a page. My book, at $22.84 for 471 pages, is less than a nickel a page. So my new book’s better per pound. I actually worked a little compiling my book, making logical groupings, picking relevant articles, creating chapter headings, the whole nine yards (never did figure out how to make a cover from an existing Wikipedia image, though). The exercise showed me the limits of Wikipedia as a book-making resource: the individual articles are fine for what they are, some are wonderful, and editing them in a somewhat logical flow has some merit. However, there’s no coherence to the final product and there are large gaps between one article and the next. How to generate rays for a given camera? Sorry, not in my book.
Still, it was great to learn of PediaPress and the ability to make my own Wikipedia book for free. Poking around their site, I even found a book on 3D computer graphics, called 3D Computer Graphics (catchy, neh?). Seeing others making books, I decided to share my own, so now it’s official. Mind you, I haven’t actually read through my book, nor even really checked the flow of articles – no time for that. I mostly grouped by subject and title after identifying likely pages. That said, I do like having a PDF file of all these articles that I can search through.
Obviously authors are not about to be replaced by Betascript books any time soon. If you want to read a real introduction to the topic, a book like Ray Tracing from the Ground Up might serve you better, even if it is a whole dime a page. This cost/benefit ratio for a good book is something I’ll never get over, that books are sold at prices that are equivalent to the cost for just an hour or two for a computer programmer’s time and yet yield so much in the right hands.







 I was waiting around a bit for my younger son’s doctor’s appointment this morning, so I decided to edit a book. I finished it just now, it’s called
I was waiting around a bit for my younger son’s doctor’s appointment this morning, so I decided to edit a book. I finished it just now, it’s called